Mobile phones have revolutionized how researchers can connect with people by enabling information to be gathered remotely. While mobile phones are often utilized to facilitate quantitative research studies, mobile phones have recently shown themselves useful for qualitative research projects too. This is important for researchers because mobile phones can make qualitative research studies affordable in locations like Africa, where traditional qualitative research methods are not cost-effective. In this post, we will discuss how qualitative research can be conducted remotely through mobile phones and provide use case examples.
Ways to conduct qualitative research in Africa through the mobile phone
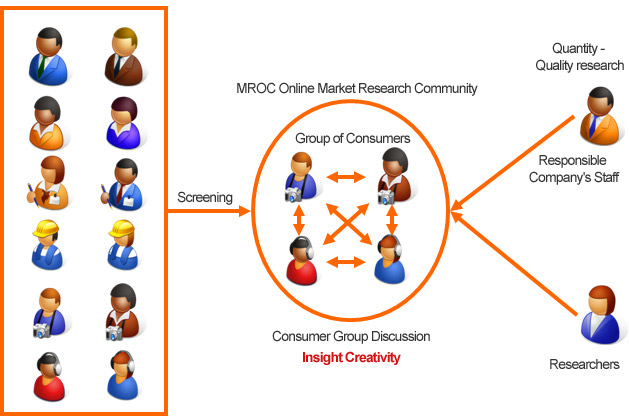
GeoPoll has had success conducting qualitative research in Africa through what are called Market Research Online Communities, which are commonly referred to as “MROCs” (/em/raks/). MROCs are not a new research method globally but because they have traditionally been conducted online through desktop computers it has been difficult to gather a representative population to participate.
In order to meet the demand for faster and more cost-effective qualitative research in Africa, Unilever’s Consumer Markets and Insights group and GeoPoll recently came up with an innovative way to conduct MROCs via the mobile phone. The idea stemmed from Unilever’s need to collect qualitative information from populations in Africa who are difficult to reach through in-person methods. By developing and piloting a process that allows MROCs to be conducted through mobile phones, Unilever has been able to gather valuable feedback on their products.
Mobile based MROCs vs. focus groups
Mobile based MROCs are similar to focus groups in that they both have moderators and provide incentives to participants, but one of the key differentiators is that the conversations in rather than a few hours. Mobile based MROCs also support multimedia use, meaning participants can be prompted to send pictures and videos to the group. This is important because it enables the research conductors to see into the lives of study participants. In the following sections of this post, examples of the importance of multimedia capabilities for MROCs will be shown.
Situational applications for qualitative research in Africa
Identifying pain points
One example of an application of an MROC would be for brands to use the interactive platform for consumers to explain their pain points with a certain product or service.
Similar to a focus group, MROCs have moderators that guide the discussion, as well as participants who can make comments that spur conversation. This can be useful for identifying pain points because you can see if participants agree or disagree on pain points and why.
Understanding consumers’ purchasing decisions
Through MROCs, moderators can guide the conversation to determine what aspects of a purchase are most important to the participants. For example, a moderator can ask probing questions about how price, quality, longevity, sustainability, brand name, and/or accessibility of a product impact the product they choose to purchase over the competing products.
Additionally, moderators can gather feedback on what aspect of a purchase is most likely to get the participants to try a new product or service, which is especially valuable for brands penetrating a new market.
Understanding how consumers use a product or service
MROCs are valuable for gaining an understanding of how consumers use a product or service in their daily lives. Humans by nature are resourceful creatures who can use an item intended for one purpose and adapt that product for another use. As a brand, the alternate uses of a product can be useful for product extension or brand diversification. A good example of this could be a toothpaste company finding out that their toothpaste is being used to polish kitchen fixtures or to treat acne or insect bites.
By using MROCs to gather such information, participants have the ability to provide pictures and videos from their daily lives to the group. Imagine a company that is focused on launching a revolutionary new kitchen gadget, for example. This company could ask MROC participants to video themselves cooking a family meal and send it to the group. The study organizers can then see first-hand how consumers are cooking and how their new gadget can fill the consumer’s unique needs, which also helps marketers position the product when it goes to market.
Takeaways
MROCs are a tool for research studies that can be used creatively to accomplish a wide variety of goals. The ability to use mobile-based MROCs in African markets is a new development that opens up a world of possibility for qualitative research studies, which have traditionally been too costly to justify.
Today, conducting qualitative and quantitative studies in Africa is easier than ever before, and GeoPoll has the capacity to facilitate both for your organization. To learn more about our capabilities, contact us today.